A 63-year-old actuary presented with painful dysphagia.
-
1. What are the common causes of dysphagia?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Dysphagia can be divided into oesophageal dysphagia and oropharyngeal dysphagia.
Oesophageal dysphagia:
- Achalasia
- Oesophageal spasm
- Stricture
- Radiotherapy
- Foreign body
- Scleroderma
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD)
- Cancer (oesophagus or extrinsic from lung/mediastinal tumours)
Oropharyngeal dysphagia:
- Neurological disorders (multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, CVA, spinal cord injury)
- Pharyngeal diverticulum
- Tumours of oropharynx (and their treatment)
-
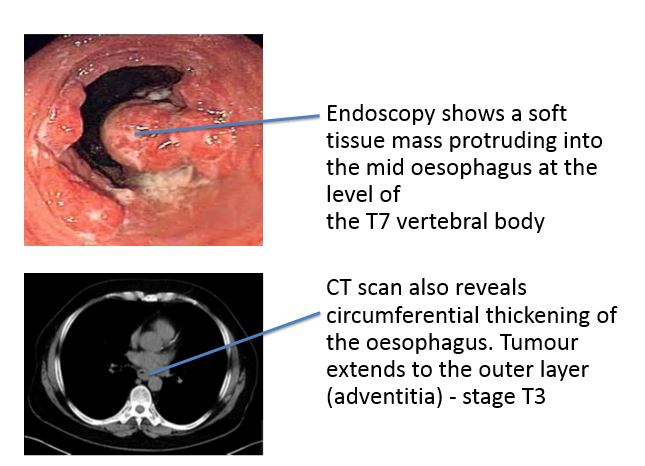
2. What do the endoscopy and CT scan show?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Endoscopy revealed a mid-oesophageal adenocarcinoma and staging investigations confirmed T3N0M0 disease.
-
3. What is the relationship between the site of the oesophageal cancer, its histological subtype and risk factors?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Upper two-third of oesophageal cancers are usually squamous cell tumours that represent about 25% of all oesophageal cancers and are associated with smoking and alcohol.
Tumours of the lower one-third of the oesophagus are more common and are usually adenocarcinomas. They are associated with gastro-oesophageal reflux (GORD) and Barrett’s oesophagus.
He received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by total oesophagectomy and gastric pull-up. This is a two-stage Ivor Lewis approach with laparotomy and mobilization of the stomach followed by a right thoracotomy with resection of the tumour and oesophago-gastric anastomosis.
Two weeks post-operatively he developed shortness of breath and a fever.
-
4. What post-operative complication does the chest X-ray, CT scan and Gastrografin swallow show?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Post-operative anastomotic leak following Ivor Lewis oesophagectomy and gastric pull up, causing large right pleural effusion.
In addition to anastomotic leaks, common post-operative surgical complications of oesophagectomy include infection, strictures and less commonly fistulas.
He had a further thoracotomy and surgical repair of the anastomotic leak and recovered remarkably well.
-
5. What are the options for fertility conservation?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
- *Egg harvesting (at present ovum storage remains an unreliable method for routine usage and requires ovarian stimulation prior to egg harvesting, which introduces a delay prior to starting chemotherapy and is relatively contraindicated in breast cancer)
- *Ovarian strip cryopreservation (experimental strategy that attempts to harvest ova without ovarian hyperstimulation and the delay that it entails)
- *Ovarian suppression (use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) suppression during chemotherapy has been used in an attempt to reduce oocyte damage)
- Storage of fertilized ova (storage of embryos is the most reliable method of conserving fertility in women)
- Egg donation (donor eggs fertilized by chosen sperm and implanted into the uterus)
- Embryo donation (donor embryos implanted into the uterus)
*currently viewed as experimental
-
6. What are the three most common psychological effects in breast cancer survivors?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
- The Lazarus syndrome (difficulty returning to normal mundane life)
- The Damocles syndrome (fear of cancer recurrence and terror of even trivial symptoms)
- The Survivor syndrome (guilt about surviving cancer where others have died)


