A 22-year-old woman from Eritrea presented with a rapidly enlarging lump on the side of her face. Over the last fortnight she had developed night sweats and fevers.
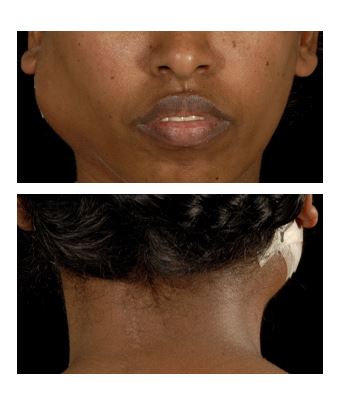
She is referred by her GP to an ENT surgeon who suspects a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL).
-
1. What are the most common subtypes of NHL?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
In terms of clinical practice, the most significant divisions are into high- and low-grade lymphoma. High-grade lymphoma is three to four times more common than low-grade lymphoma. The most common subtypes in order are:
| Pathological subtype |
Grade |
Percentage of NHL diagnoses |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBL) |
High grade |
31% |
| Follicular lymphoma (FL) |
Low grade |
22% |
| Marginal zone lymphoma (MZ) |
Low grade |
8% |
| T-cell lymphoma (TCL) |
Low or high grade |
7% |
| Small lymphocytic lymphoma |
Low or high grade |
6% |
| Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) |
High grade |
6% |
| Burkitt’slymphoma (BL) |
High grade |
3% |
After nasendoscopy to exclude an aerodigestive primary, she has a lymph node excision and bone marrow aspirate and trephine biopsy.
-
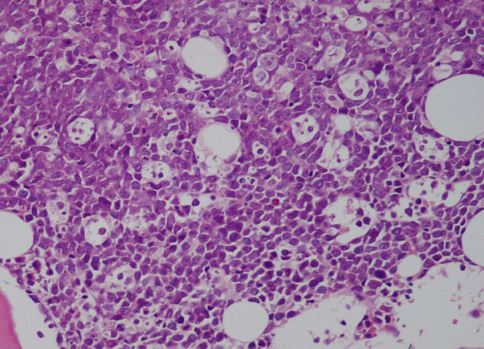
2. What does her bone marrow biopsy show?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Her bone marrow is almost completely replaced by an infiltration of small non-cleaved abnormal lymphocytes of Burkitt’slymphoma. This is confirmed by immunostaining for CD20, CD10 and K67 (MIB-1).
-
3. What chromosomal translocation is associated with Burkitt’slymphoma?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
t(8;14)(q24;q32); t(2;8)(p12;q24); and t(8;22)(q24;q11). These three reciprocal chromosomal translocations juxtapose the immunoglobulin gene promoters (IgH at 14q32 or light chains at 2p12 and 22q11) with the c-myc oncogene at 8q24. The result is overexpression of the c-myc oncogene, a transcription factor for cell cycle progression/proliferation.
-
4. What stage disease does she have?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
Stage IVB (nodal and bone marrow involvement, hence stage IV. B as night sweats and fevers
A final diagnosis of stage IVB Burkitt’slymphoma was made. Her HIV serology was negative. She was treated with two cycles of alternating R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC intensive chemotherapy and intrathecal chemotherapy prophylaxis. Each cycle was complicated by febrile neutropenia despite prophylactic G-CSF. She achieved a complete radiological remission confirmed by PET-CT imaging.


